REPOSTED from Uniqtech Medium with Permission
Anaconda is a technical package manager that is especially useful for data scientists. It can save hours of configuration for windows users. It is a bit bulky but it is data scientists’ friend and must have toolkit in academia. Researchers use anaconda to manage their packages, instead of Python pip all the time.
Are you working on an Udacity nanodegree? Are you using Kaggle for data competitions? Are you doing graduate level research and studies? Anaconda may be your friend!
Staff writer Sun says she uses anaconda to install all packages on her windows gaming computer, so that she can easily use the GPU to train her neural networks. She’s a Mac user and want to spend minimal time configuring and setting up a development environment on windows. It just works. All her Jupyter Notebooks run, and it was easy to use CUDA to train her models on GPU.
Convention
$ prefix means it is a command line command which distinguishes from a python or Javascript line of code. Don’t copy and paste the dollar sign when using our cheatsheet.
Prefer a PDF version of the cheatsheet? Let us know in the comments or email us at hi@uniqtech.co
Installation and Uninstall
Miniconda is a lite version (light version) of anaconda. It takes less space but has the essentials of a data scientist toolset. Udacity sometimes suggests its students install miniconda.
Forcefully remove miniconda or anaconda. Use only if you know what you are doing.
~/ is the home path on Mac. You need to locate where your miniconda is installed on your computer first.$ rm -r ~/miniconda
Anaconda offers an IDE called Spyder. It’s a desktop, visual GUI, which is easy to use and navigate. Pro tip: Use
command+M to open the matrix helper to quickly enter matrix data.
List all installed conda package
$ conda list
Install opencv with conda. This command does not work all the time. If fails, search stack overflow.
$ conda install -c conda-forge opencv
Using Anaconda
Anaconda Environments
List all environments. Forgot the name of the environment you created? Use this command to list all environments.
$ conda env list
Create an anaconda environment.
create -n creates a new environment. We also specified the version of python we want to use python=3 . We also added the package we want to install as a suffix.$ conda create -n my_env numpy
Activate an anaconda environment. How to activate Anaconda environment? Use the command below
$ conda activate my_env
Use Anaconda to Install Data Science Packages
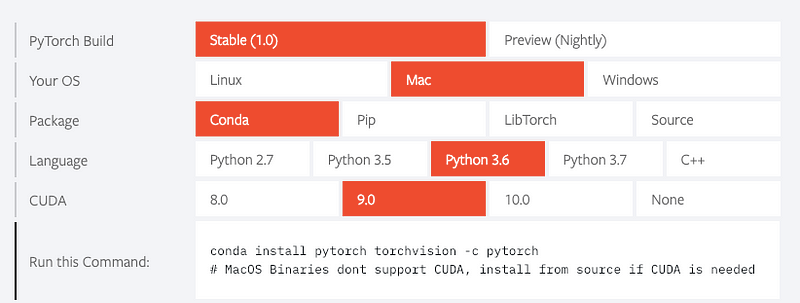
Use Anaconda to install Pytorch (check the Pytorch documentation for the latest and greatest). Only run this command after you finished the recommended anaconda initial install.
$ conda install pytorch torchvision -c pytorch
See the Pytorch documentation above. You can toggle and check how to instal using Pip as well if that’s easier.
Advanced Use of Anaconda
Using Anaconda in production | Using Anaconda for Reproducible Research
Exports Requirements | Creates Environment Yaml File
It may be apparent now that conda uses
.yaml to manage configuration and requirement files similar to modern Ruby on Rails and Node.js, front end development best practice.$ conda env export > environment.yaml $ conda env create -f environment.yaml
Removing Packages
Would you like to keep your dev environment lean and clean? Remove anaconda packages use the command below.
$ conda remove package_name_1 package_name_2 $ conda remove scipy curl
Updating Jupyter Notebook and its Kernel
conda update jupyter Update the kernel to the latest version of Python conda install python=3 Make Jupyter Notebook aware of new anaconda environment ipython kernel install --name my_env_name --user . So the kernel can be set. Additional Resources:
- Attend anaconda con conference